Architecture
Vortex is a production-ready Drupal project template designed to simplify onboarding, unify workflows, and ensure long-term maintainability.
This page provides a high-level overview of how the template is structured, how its components work together, and how your project benefits from its architecture.
Design Principles
Vortex is guided by principles that prioritize simplicity, visibility, and maintainability:
- Simple is better than complex: The template encourages clarity, even in customizations.
- Use standard tools: Wherever possible, Vortex follows upstream conventions and avoids reinvention.
- Avoid silent errors: Misconfigurations should fail loudly.
- Readability counts: Code and configuration are meant to be understood.
- Explicit logging helps: Scripts log every major step, so it’s easy to follow what’s going on.
System Components
The system is made up of several modular pieces that work together:
- Local development environment
- Drupal management
- Code quality and testing tools
- Continuous integration workflows
- Hosting provider configurations
- Automated dependency updates
- Project documentation
- Workflow scripts to connect components
You can see how these parts connect in the diagram below:
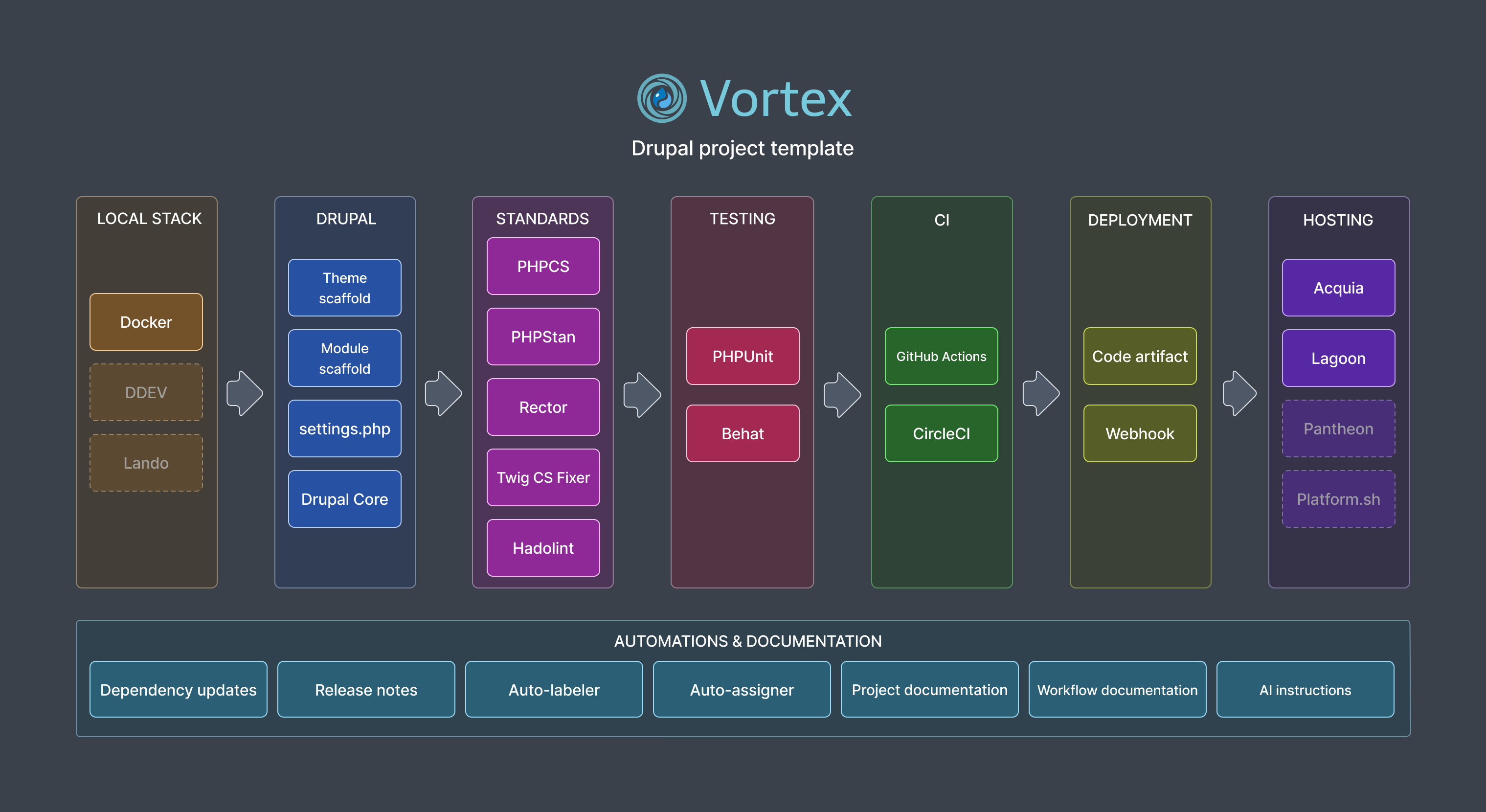
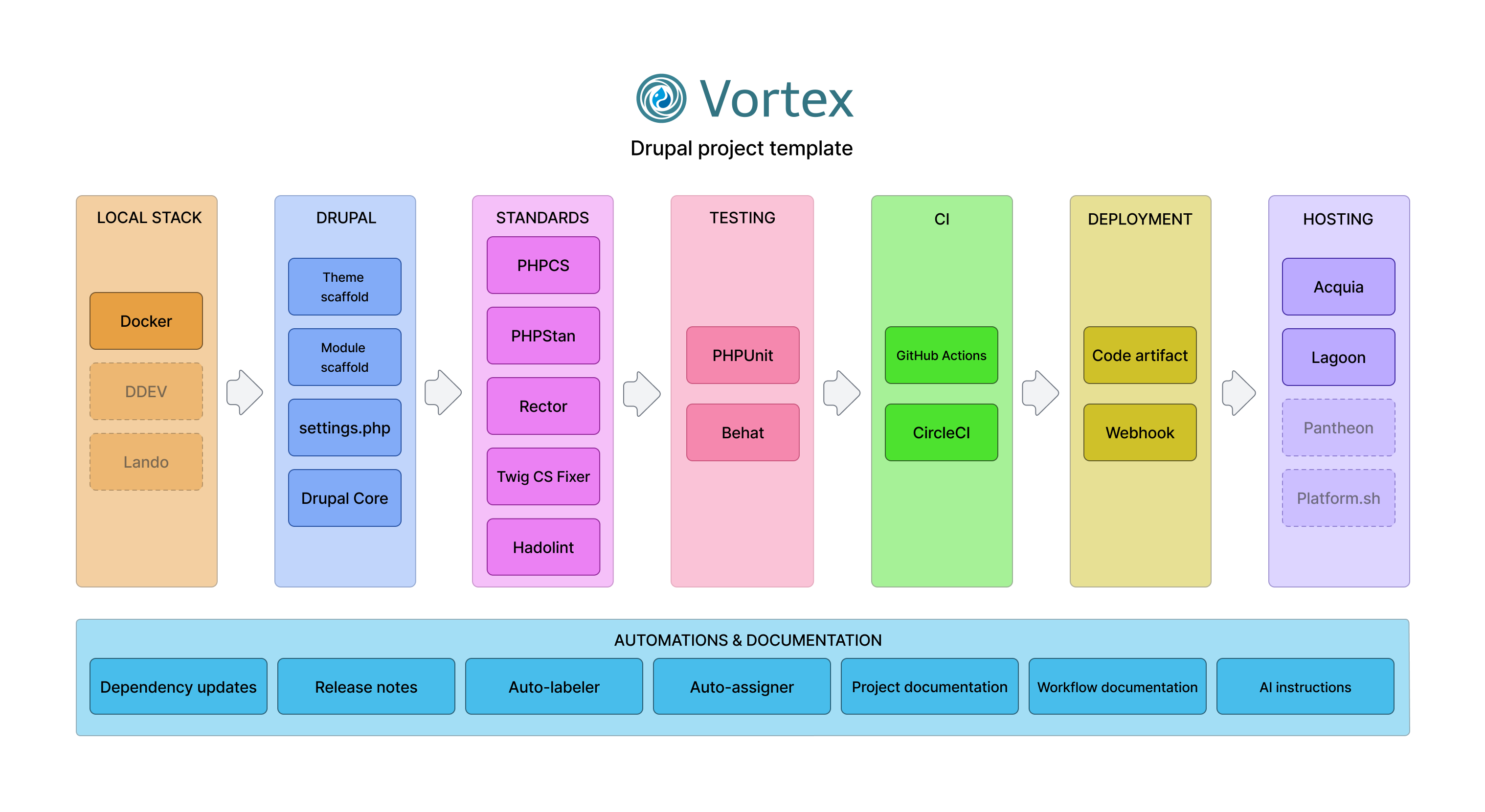
Local Development Environment
Your project includes a containerized local environment using Docker Compose and production-grade Lagoon images. This ensures consistency between local, CI, and hosting environments.
To simplify command usage, we use Ahoy as a wrapper. It lets you run complex workflows like provisioning, testing, or database imports with short, easy-to-remember commands.
Drupal management
Provisioning
The provisioning process is central to how Vortex works. Instead of manually running Drush commands, you run a single provision script. This script handles:
- Importing a database (or initializing from a profile)
- Running updates, config imports, cache rebuilds, and deploy hooks
- Executing post-provision custom scripts
Because provisioning is centralized, it runs exactly in the same way in every environment: local, CI, or hosting. This eliminates "works on my machine" problems and makes the process predictable for everyone.
➡️ See Drupal > Provision
Module and Theme Scaffolds
We include examples of a custom module and theme, each fully integrated with tests. These show you how to:
- Structure custom features
- Write functional, kernel, and unit tests
- Connect theme assets to a build pipeline
Use these scaffolds as starting points for your own work.
➡️ See Drupal > Module Scaffold and Drupal > Theme Scaffold
Settings Management
Vortex includes a structured way to manage Drupal settings per environment. Here's how it works:
- The environment type (e.g. local, CI, stage) is automatically detected based on your hosting provider.
- Configuration overrides are stored in
includes/modules/with logic per environment inside each module-specific file.
This structure gives you clarity, avoids config sprawl, and lets you remove a module’s settings cleanly when no longer needed.
➡️ See Drupal > Settings
Code Quality and Testing
Vortex ships with pre-configured tools for maintaining code quality:
- PHP CodeSniffer (phpcs)
- PHPStan
- PHP Mess Detector (phpmd)
- Twig CS Fixer
You’ll also find scaffolds for:
- PHPUnit: Unit and kernel testing
- Behat: Behavior-driven testing with screenshot capture and extra steps
➡️ See Tools > PHPStan, Tools > PHPCS, Tools > Behat, and Tools > PHPUnit
Continuous Integration Workflows
Vortex supports GitHub Actions and CircleCI. You choose which one to use in your project. The workflows include:
- Database download and caching (for faster builds)
- Full site provisioning in CI
- Running code quality checks
- Running unit, functional and behavior tests
- Triggering deploys when tests pass
Each continuous integration configuration mirrors what happens locally and in hosting to ensure uniformity.
➡️ See Continuous Integration
Hosting Integrations
Out of the box, Vortex supports Acquia and Lagoon hosting. These integrations:
- Trigger provisioning with the same steps used locally and in CI
- Provide deployment workflows suited to each platform
You can use Vortex with other platforms too, but these are first-class integrations.
➡️ See Hosting
Automated Dependency Updates
Vortex includes configuration for RenovateBot to automate dependency upgrades:
- Critical updates checked daily
- Regular updates run weekly
- PRs include changelogs and pass through your continuous integration pipeline
You can host RenovateBot yourself or use the cloud version, and you can tweak the schedule as needed.
➡️ See Tools > Renovate
Documentation & Onboarding
Vortex includes centralized documentation (what you’re reading now), as well as a scaffold for adding project-specific docs within your own repository.
Workflow Scripts
A workflow is a sequence of steps to achieve a goal. In Vortex, those are
defined via POSIX-compliant Bash scripts in scripts/vortex.
These scripts:
- Run identically across local, CI, and hosting
- Support environment variables to adapt behavior
- Are modular and easy to extend
Customizing workflows
All scripts support configuration via environment variables, allowing workflows to be easily adapted to specific project or environment needs.
During initial project setup, .env file is updated with project-specific
values like project name, email etc. Then, environment variables (secrets,
tokens, etc.) are set in CI or hosting environments.
Refer to the Workflows section for more details.
Router scripts
Most Vortex commands are implemented as router scripts entry points like
download-db.sh or deploy.sh—that dynamically invoke a more specific logic
for your setup, based on configuration or environment variables.
For example:
download-db.shis a router script that downloads a database from any supported hosting provider or custom location without needing to know the specifics of each provider.deploy.shis a router script that deploys code to any hosting provider in a consistent manner, regardless of whether it's Acquia, Lagoon, or another platform.
Script architecture diagram


➡️ See Workflows